Vertical Housing: Enhancing Urban Living Through Social Sustainability
Course: B Arch Thesis Project, Anna University
Overview:
Process & Contributions:
The thesis project addressed the housing crisis in urban Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, by proposing a vertical residential community that integrates affordability, density, and sustainability. With urban land scarcity and population growth driving high-rise development, the project explored architectural solutions that foster social cohesion, accessibility, and inclusive living.
1. Research & Problem Identification
Conducted a literature review on vertical housing models and social sustainability principles, focusing on affordability, shared living, and well-being.
Researched case studies including Amanora Future Towers (Pune) and 8 House (Denmark), drawing lessons in spatial design, circulation, and community infrastructure .
Carried out surveys and interviews with 50+ urban residents, identifying spatial and social needs such as shared gardens, co-working areas, and inclusive amenities.
2. Site Analysis & Zoning
Selected an 8.55-acre site in Pallavaram, Chennai, chosen for proximity to IT hubs, retail, and metro connectivity .
Conducted climate, vegetation, and land use studies, ensuring optimal orientation, natural ventilation, and integration with the surrounding ecosystem.
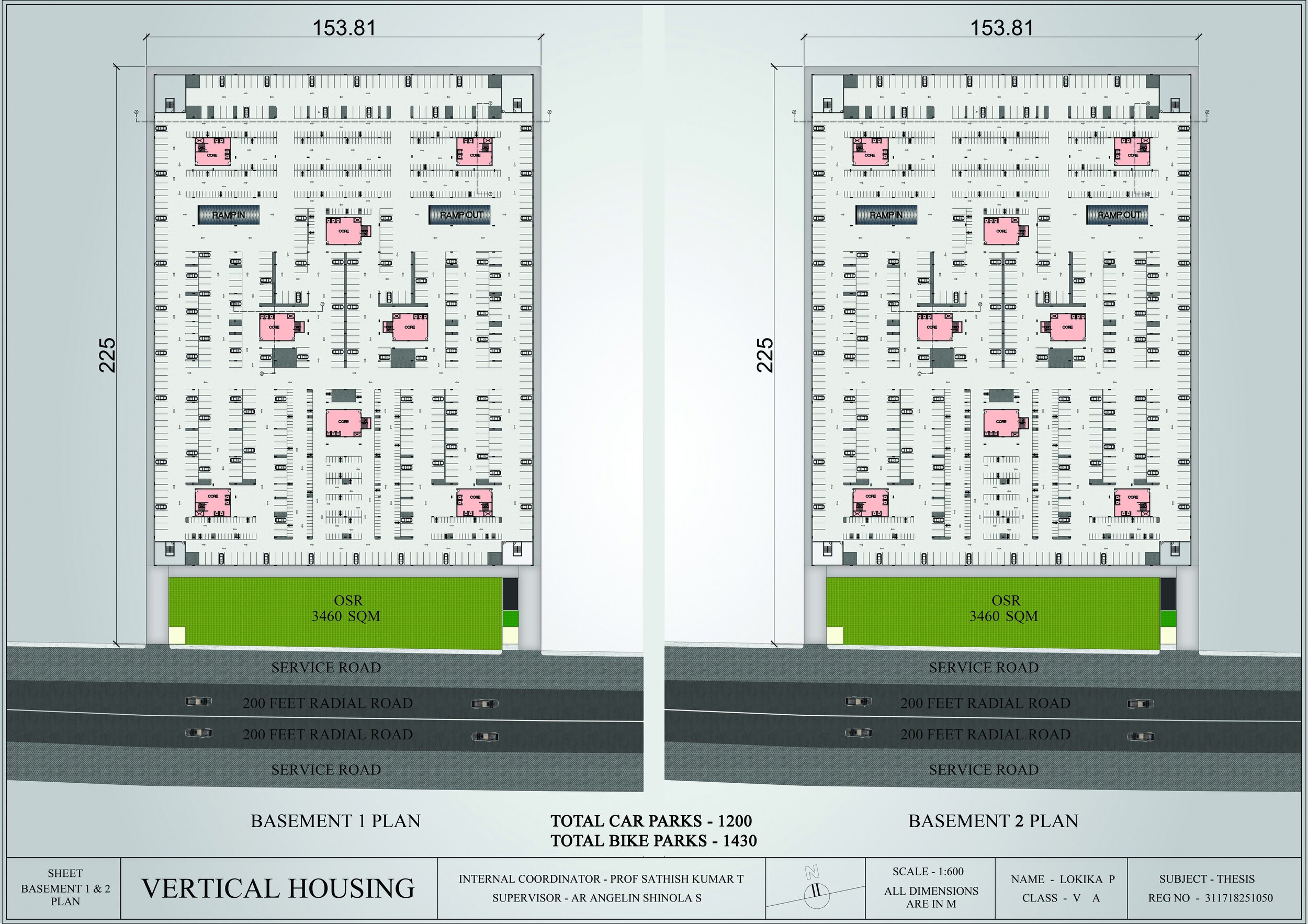
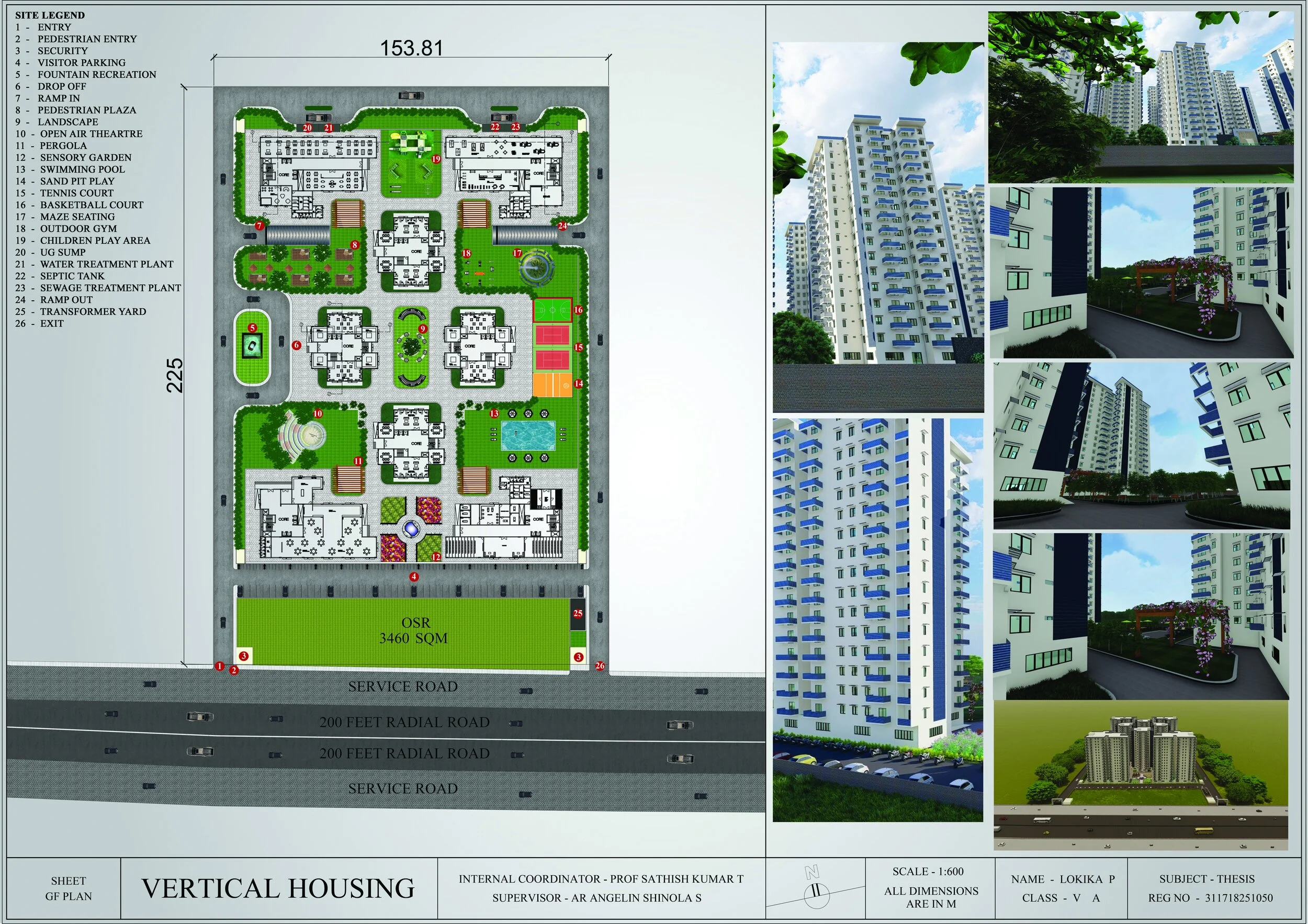
Developed an area statement and zoning strategy to balance residential density with communal green and public spaces .
3. Design Development
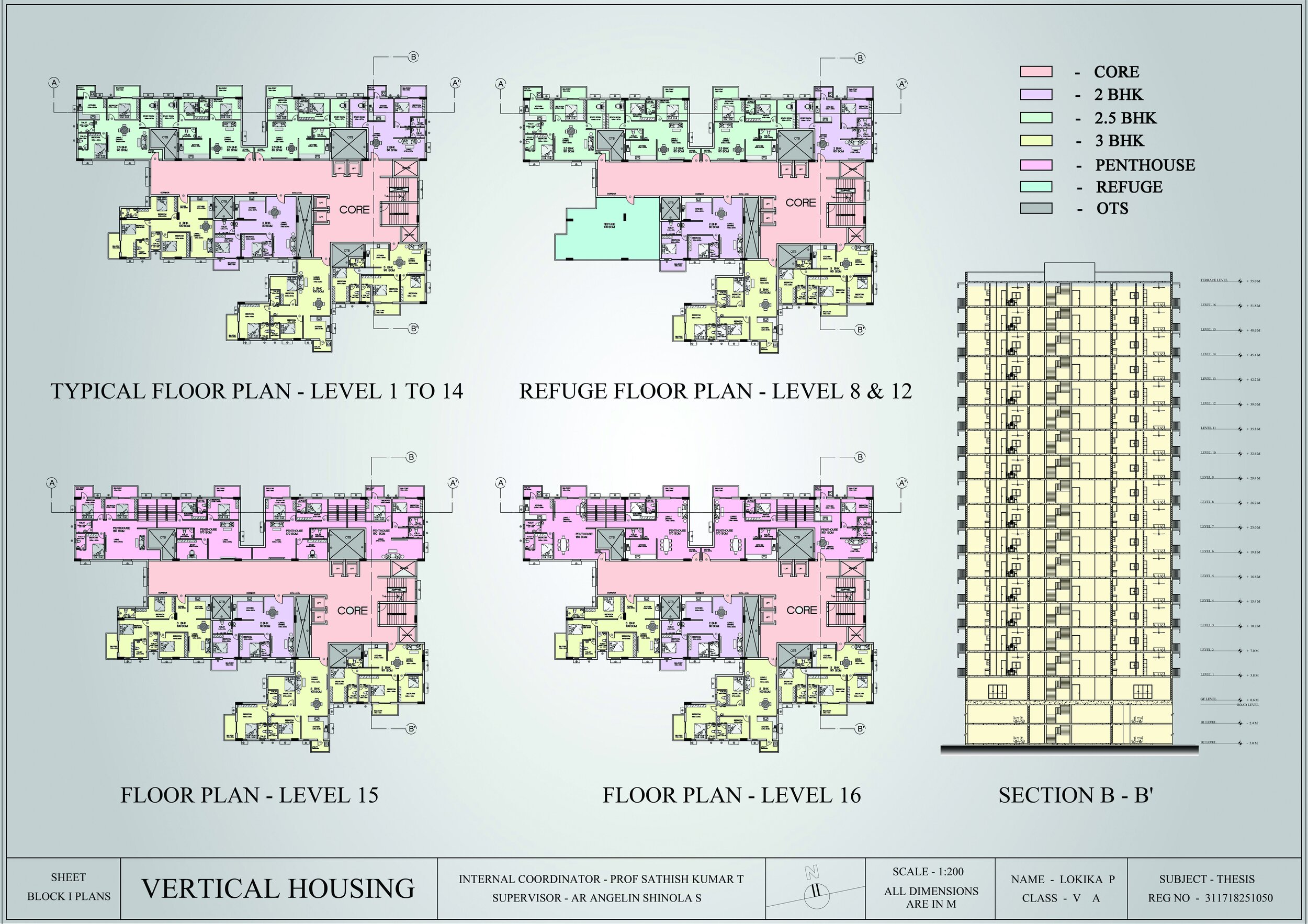
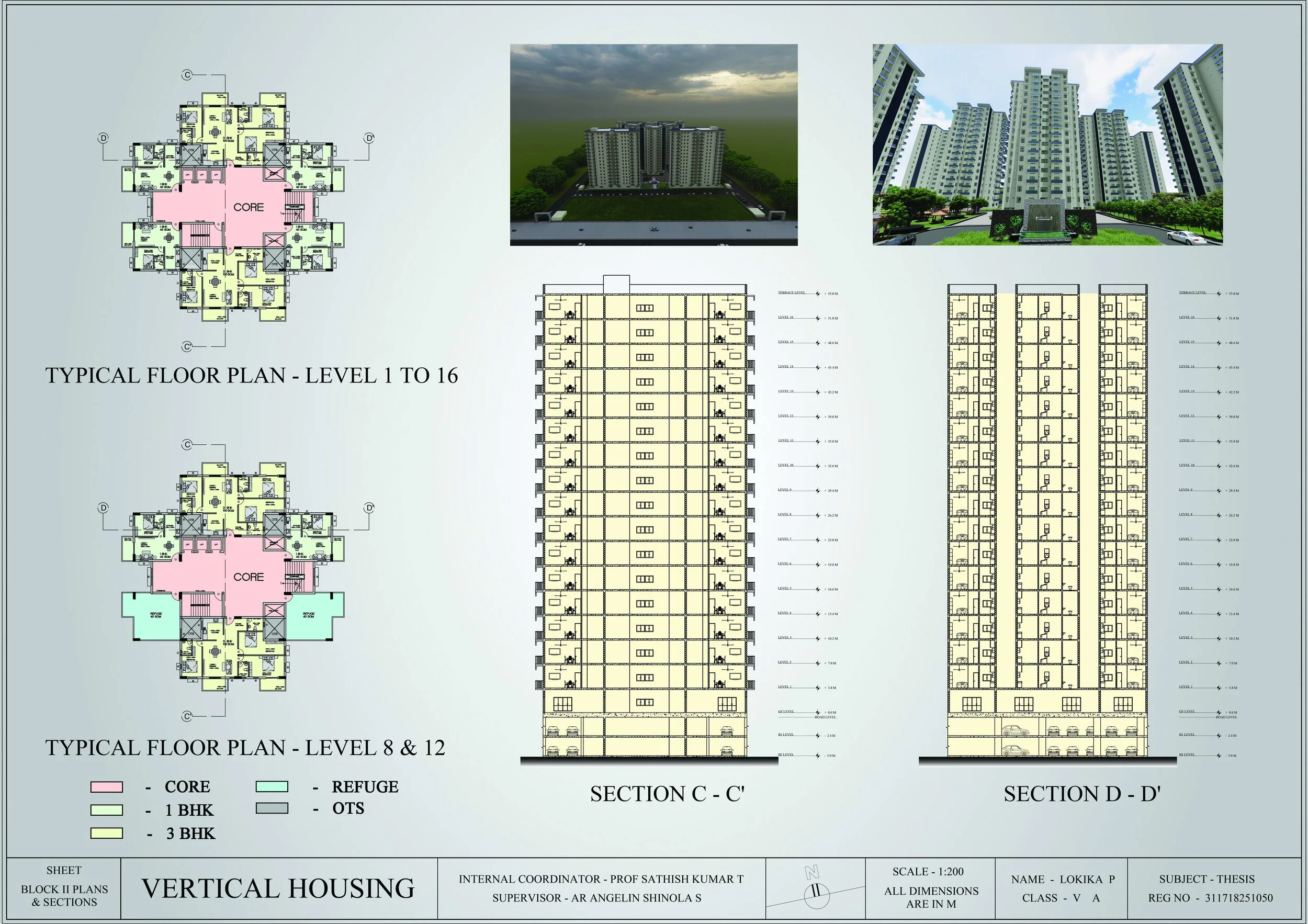
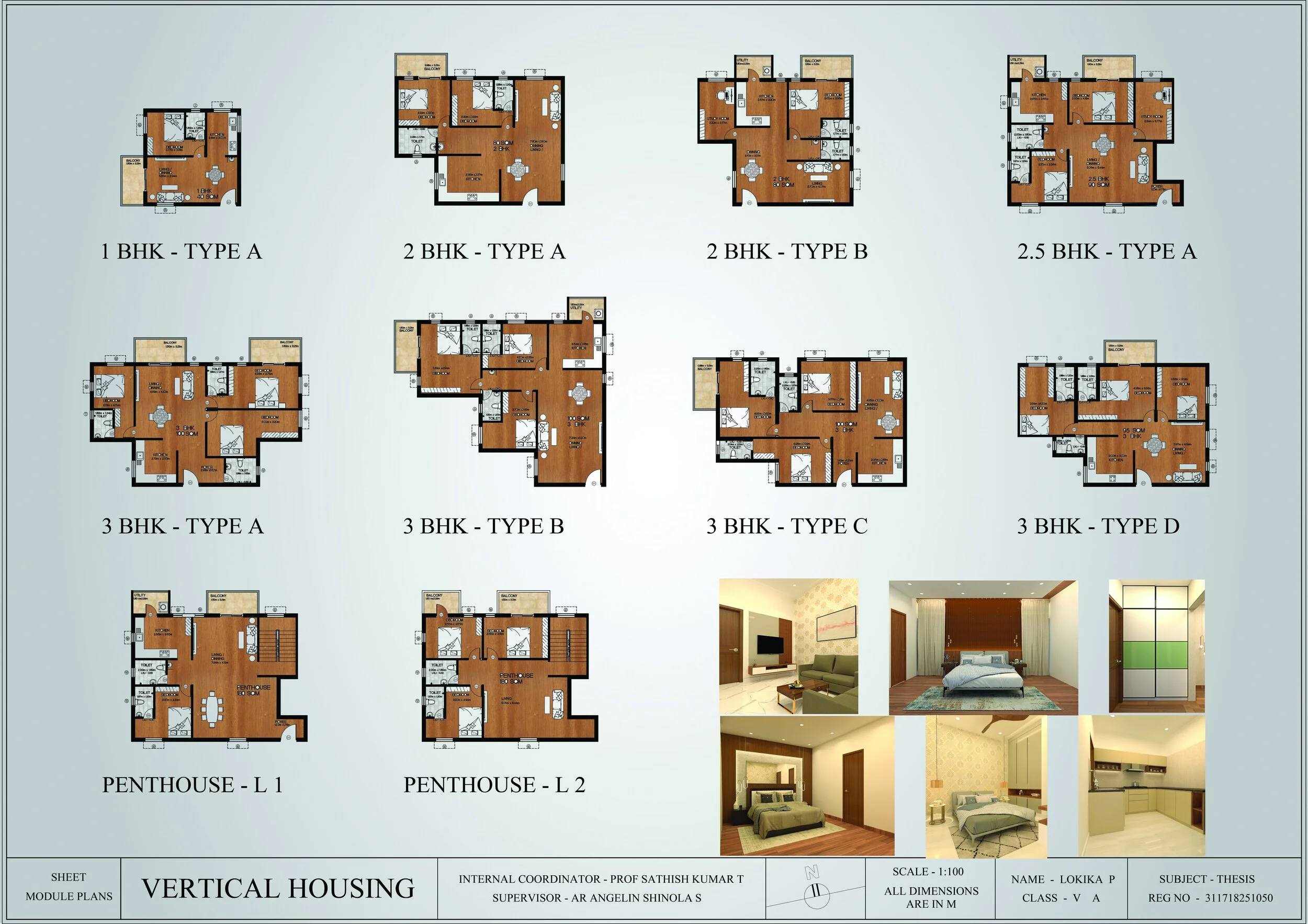
Applied information architecture and spatial zoning principles to design three housing typologies (studio, 1BHK, 2BHK, 3BHK) tailored to different user groups.
Designed communal spaces (gardens, co-working hubs, pedestrian plazas, sky courts) to increase interaction and social sustainability.
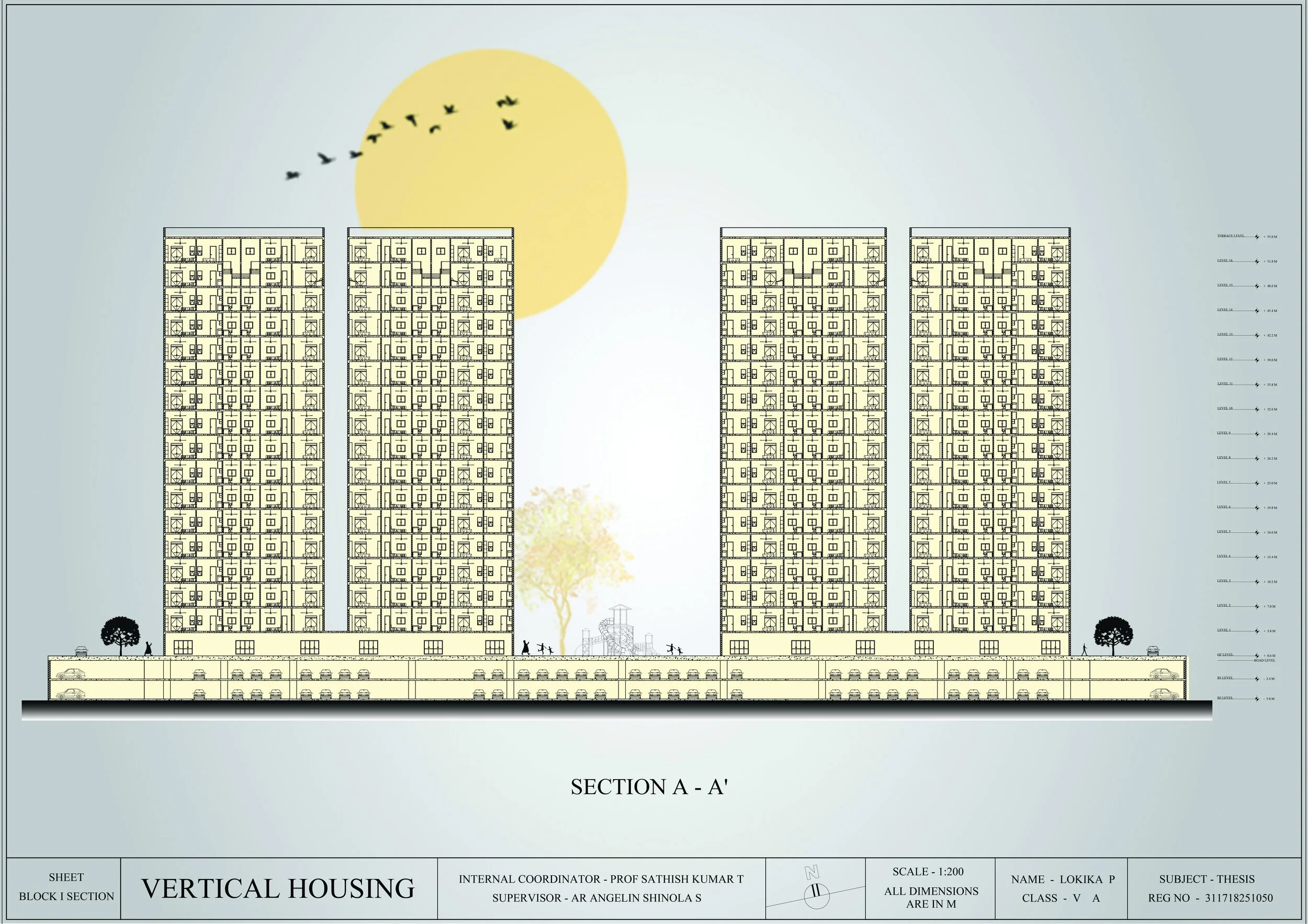
Created detailed plans, modules, and circulation strategies using SketchUp, Lumion, and AutoCAD.
Outcome & Impact:
Proposed a multi-residential vertical precinct with integrated public plazas, green corridors, and semi-open social spaces, addressing both density and quality of life.
Improved accessibility, efficiency, and inclusivity through flexible unit layouts and shared facilities.
Contributed to urban housing discourse by demonstrating how vertical housing can balance affordability, sustainability, and social well-being in high-density Indian cities.